



Health Information


Common Foot Problem in Children: Bowlegs
Common Foot Problem in Children: Bowlegs
Another common foot problem in children is “Bowlegs (genu varum).”
What are bowlegs?
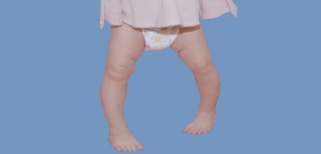
Bowlegs (genu varum) is a condition in which a child’s legs curve outward at the knees. When a child with bowlegs stands with their toes pointing forward, their ankles may touch, but their knees remain apart.
Bowlegs are considered a normal part of growth in babies and toddlers. In young children, bowlegs are not painful or uncomfortable and do not interfere with a child’s ability to walk, run, or play.
Children typically outgrow bowlegs sometime after 18 to 24 months of age. In rare cases, bowlegs may be a sign of a growth disorder.
What are the symptoms of bowlegs?
- Knees curve outward
- Awkward walking pattern
- Toes point inward in some cases (known as in-toeing)
- Clumsiness or frequent tripping
What causes bowlegs?
- Bowlegs often develop in a child’s first year as part of natural growth for no known cause. Some babies are born with bowlegs.
- This can happen as the baby grows and the space inside their mother’s womb gets tighter, causing the leg bones to curve slightly. In most cases, children’s legs straighten out as they grow and develop.
- Certain conditions, such as Blount’s disease, metabolic disorders, and bone malformations, may cause a child’s legs to bow.
When should parents be concerned about bowlegs?
Most children with bowlegs do not need medical treatment. Your child’s doctor will observe your child over time to ensure their legs straighten out on their own. If your child has bowlegs along with any of the following symptoms, they may have a more serious condition:
- Bowlegs that continue to get worse after the age of 2
- Asymmetric appearance of the bowing
- Limp when walking
- Knee or hip pain
- Short stature (below the fifth percentile)
If your child has any of these symptoms, you should seek guidance and advice from a professional physiotherapist or medical expert. Make an appointment to talk to a podiatrist to obtain a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Related Services:
- General Podiatry
- Paediatric Foot Conditions
- 3D Scanning for Orthotics
- Custom Orthotic Prescription
- Gait Analysis
Futher reading:



