Health Information


PIP Joint Injuries
Finger Injuries - PIP Joint Injuries
Mechanism of Injury
A dorsal dislocation occurs through hyperextension and axial load.
A volar dislocation or central slip injury occurs with a flexion force.
Symptoms
PIP joint instability or mal-alignment, or both.
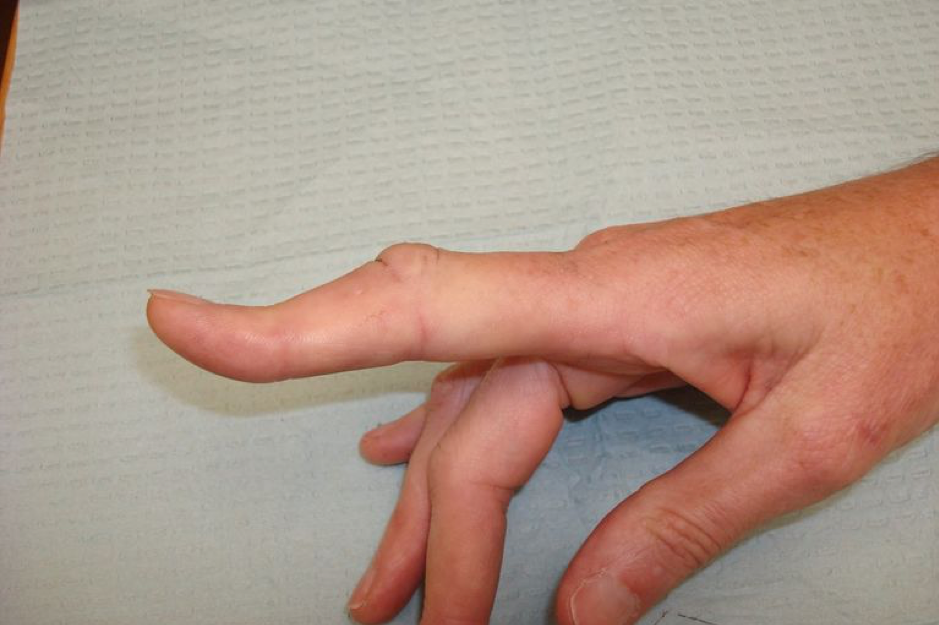
If the central slip is injured, there will be a loss of active extension or boutonniere
deformity, or both.
|
Dorsal dislocation / Volar plate injury |
Boutonniere deformity following central slip injury |
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by assessing joint laxity, range of motion and with an x-ray.
Referral
Referrals shall be made as soon as possible. If the PIP joint was dislocated, a referral should be made post-reduction immediately.
Management
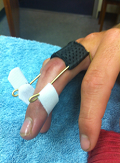
For a volar plate avulsion fracture or dorsal dislocation, the PIP joint is protected with a splint or buddy taping depending on the stability of the joint. Volar plate avulsion fractures are stabilised in flexion and may require to be splinted in this position.
As soon as comfortable or stability allows, commence active PIP joint extension to
prevent a fixed flexion deformity.
For volar dislocations, central slip injuries or collateral ligament injuries the PIP joint is
splinted in extension.
Mobilise into flexion if no central slip avulsion fracture.
Oedema management and joint protection are imperative to a good outcome.
Splinting Options
|
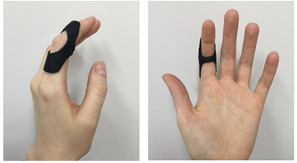
Dorsal finger splint for volar plate avulsion fracture |
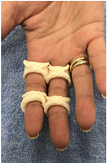
Oval 8 splint for dorsal dislocation |
|
Buddy splint |
Extension splint |
Mobilising splint |