Health Information


De Quervains tendinopathy
De Quervain’s Tendinopathy
Mechanism of Injury
De Quervain’s tendinopathy is a painful condition that affects the thumb tendons that lift the thumb up (extensor pollicis brevis) and away from the palm (abductor pollicis longus) as well as the tendon sheath. At the wrist, these tendons run through a tight tunnel known as the first dorsal compartment which is part of the extensor retinaculum. Inflammation or changes to these tendons, the sheath and or retinaculum can result in pain, and restricted movement of the thumb and wrist. Although the exact cause of de Quervain’s tendinopathy is not known, forceful and repetitive thumb and wrist movement can make it worse. A direct injury to the wrist and thumb tendons can also lead to this condition.
Symptoms
- Pain at the wrist at the base of the thumb
- Pain aggravated with gripping and pinching objects and when moving the wrist towards the side of the little finger
- Swelling over the first dorsal compartment (thumb side of the wrist)
- Reduced thumb and wrist motion
- A ‘catching’ sensation when moving the thumb
Diagnosis & Risk Factors
De Quervain’s tendinopathy is most common in women between the ages of 30 and 50. Women are more at risk of this condition as it can be associated with pregnancy and caring for babies. This can be due to hormonal changes as well postures sustained with breastfeeding or frequently picking up babies under their arms.
Imaging is not typically required to confirm the diagnosis. A thorough physical assessment including observing and palpating thumb and wrist movement is required. Pain is commonly experienced with resisted thumb extension and abduction.
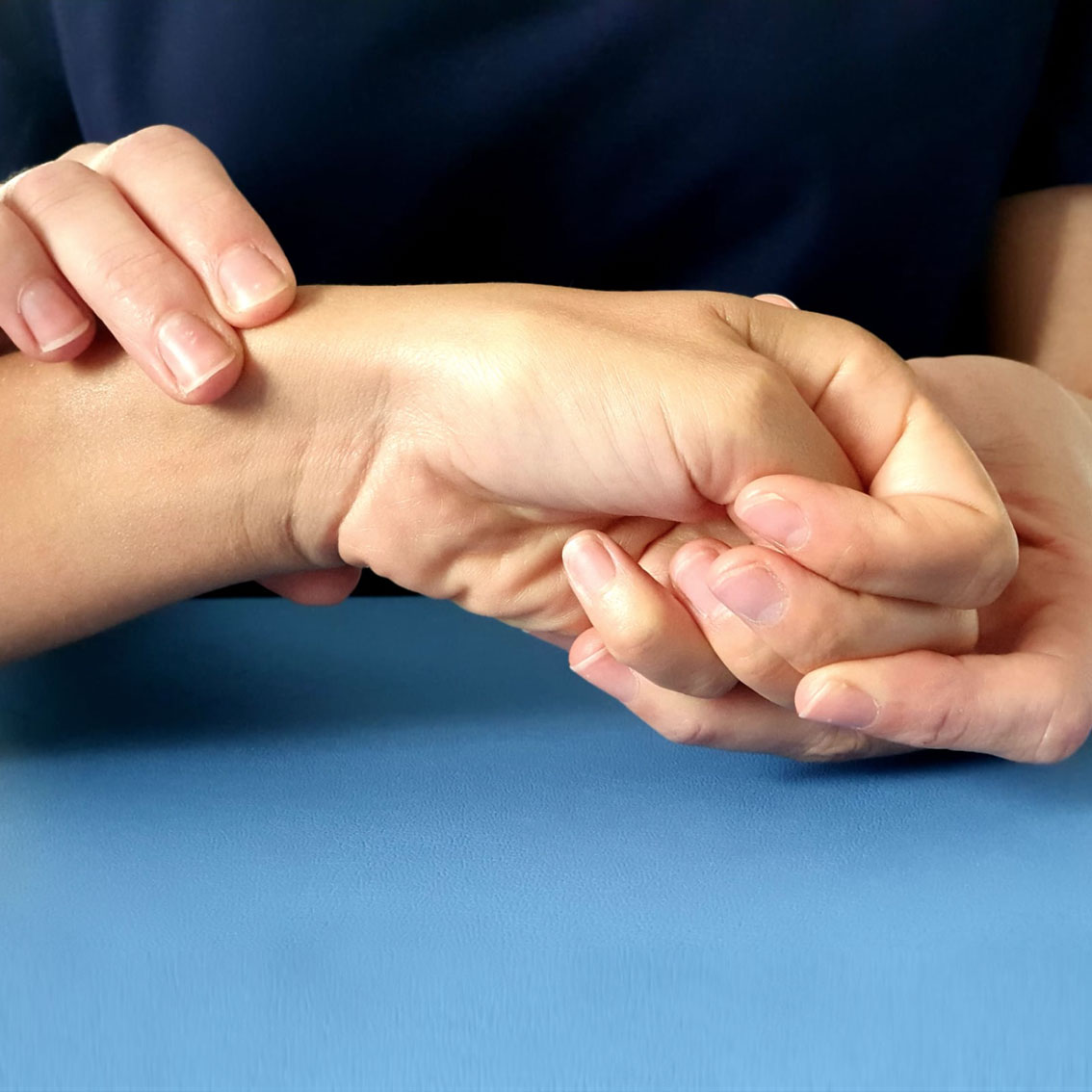
A Finkelstein’s test can be performed in which the patient is asked to grasp their thumb in their palm with their fist. The examiner then bends the patients’ wrist towards their little finger. A positive test causes pain on the thumb side of the wrist.
|
Finkelstein’s test |
Referral
A referral should be made as soon as symptoms appear as symptoms typically get worse if left untreated.
Conservative Management
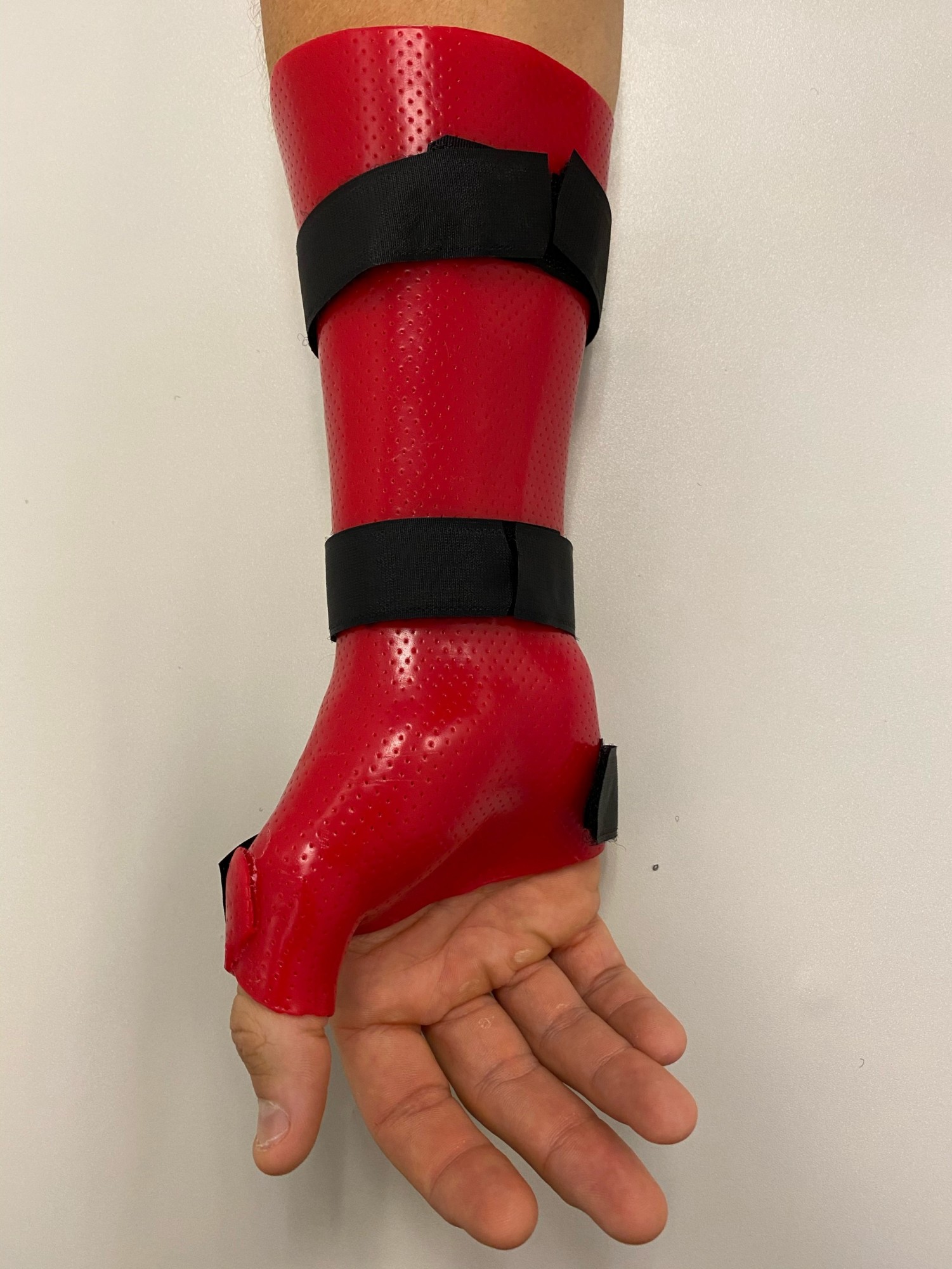
- A custom made thermoplastic wrist and thumb splint is commonly required between 2-6 weeks to limit wrist and thumb movement and to allow the tendons to rest.
- Pain and oedema management such as taping.
- Advice regarding activity modification.
- As pain subsides a graded exercise program to regain thumb movement and strength will be prescribed.
In conjunction with the above treatment a corticosteroid injection may also be recommended to help decrease pain and inflammation.
|
Long thumb spica splint |
Post Surgical Treatment
If symptoms do not improve with conservative management, a referral to a hand surgeon may be required. Surgery involves the release of the first dorsal compartment to allow the tendons more space to move. Following the procedure, rehabilitation may be required including:
- Wound care including removal of sutures.
- Scar and oedema management.
- A graded exercises program to regain thumb movement and strength
- Desensitisation program.